A direct reduced iron (DRI) plant, also known as a sponge iron plant, is a crucial part of the steel industry. DRI is a highly pure form of iron that is produced through the reduction of iron ore in solid-state, without the use of coke or charcoal. This method of iron production is highly efficient and environmentally friendly, making DRI plants increasingly popular in recent years. The production of DRI involves the removal of oxygen from iron ore, resulting in the production of high-quality iron nuggets. The reduction process occurs in a direct reduction furnace, where iron ore is heated at high temperatures (typically around 800-1200°C) in the presence of a reducing agent, such as natural gas or syngas. The reducing agent reacts with the iron ore, leading to the elimination of oxygen and the formation of metallic iron. DRI plants are strategically located near sources of natural gas and iron ore, as these are the primary raw materials used in the production process. The availability of these resources plays a significant role in determining the feasibility and profitability of a DRI plant.
iron
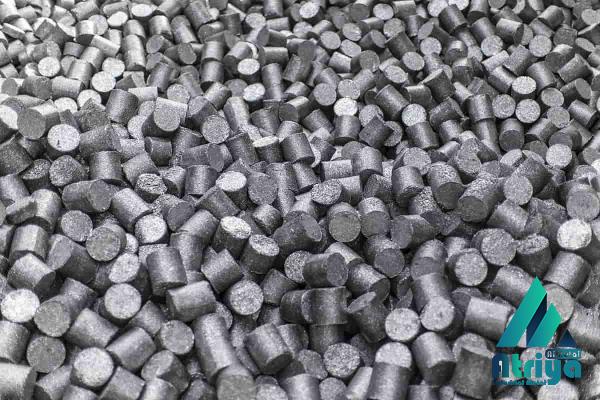 Additionally, the proximity to steel mills is also a crucial factor, as DRI is primarily used as a feedstock in electric arc furnaces (EAF) to produce steel. The direct reduction process offers several advantages over traditional blast furnace ironmaking. Firstly, DRI plants have a smaller environmental footprint compared to blast furnaces. They emit fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants, making them more environmentally sustainable. Secondly, the product produced by DRI plants, sponge iron, has a high iron content and lower impurities, making it a preferred feedstock for steelmaking. This results in improved steel quality and lower production costs. Lastly, DRI plants are more flexible and can adapt to fluctuating market demands due to their smaller scale and shorter production cycles. The process of producing DRI involves several stages. Firstly, the iron ore is mined and refined to remove impurities. The purified iron ore is then processed into pellets or briquettes to enhance its handling and transportation capabilities. These pellets or briquettes are fed into the direct reduction furnace, where they are heated and reduced to produce sponge iron. The sponge iron is then cooled and processed into various forms, such as hot briquetted iron (HBI) or cold direct reduced iron (CDRI), depending on the intended use. DRI plants require significant investments in infrastructure and technology.
Additionally, the proximity to steel mills is also a crucial factor, as DRI is primarily used as a feedstock in electric arc furnaces (EAF) to produce steel. The direct reduction process offers several advantages over traditional blast furnace ironmaking. Firstly, DRI plants have a smaller environmental footprint compared to blast furnaces. They emit fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants, making them more environmentally sustainable. Secondly, the product produced by DRI plants, sponge iron, has a high iron content and lower impurities, making it a preferred feedstock for steelmaking. This results in improved steel quality and lower production costs. Lastly, DRI plants are more flexible and can adapt to fluctuating market demands due to their smaller scale and shorter production cycles. The process of producing DRI involves several stages. Firstly, the iron ore is mined and refined to remove impurities. The purified iron ore is then processed into pellets or briquettes to enhance its handling and transportation capabilities. These pellets or briquettes are fed into the direct reduction furnace, where they are heated and reduced to produce sponge iron. The sponge iron is then cooled and processed into various forms, such as hot briquetted iron (HBI) or cold direct reduced iron (CDRI), depending on the intended use. DRI plants require significant investments in infrastructure and technology.
Specifications of iron
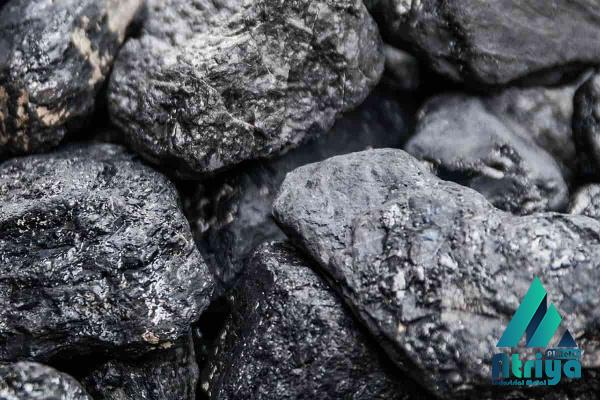 The construction of a DRI plant involves the establishment of a direct reduction furnace, gas cleaning systems, cooling systems, and handling and storage facilities for the produced sponge iron. Additionally, a reliable and cost-effective source of natural gas is essential for the operation of the DRI plant. The capital expenditure required for building a DRI plant can range from hundreds of millions to billions of dollars, depending on the plant’s size and capacity. The operational efficiency of a DRI plant is critical for its long-term success. The plant’s uptime and production rate affect its profitability and competitiveness in the market. Efficient furnace operation, consistent quality control measures, and effective maintenance practices are crucial for maximizing the plant’s productivity. DRI plants often incorporate advanced automation technology to optimize process control and minimize downtime. The market for DRI has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for steel and the need for more sustainable ironmaking processes. DRI is mainly used as a feedstock in electric arc furnaces, which are commonly used in the production of long steel products, such as reinforcing bars, wire rods, and structural sections. The use of DRI in EAFs reduces the dependence on scrap metal and lowers energy consumption, resulting in cost savings for steel manufacturers.
The construction of a DRI plant involves the establishment of a direct reduction furnace, gas cleaning systems, cooling systems, and handling and storage facilities for the produced sponge iron. Additionally, a reliable and cost-effective source of natural gas is essential for the operation of the DRI plant. The capital expenditure required for building a DRI plant can range from hundreds of millions to billions of dollars, depending on the plant’s size and capacity. The operational efficiency of a DRI plant is critical for its long-term success. The plant’s uptime and production rate affect its profitability and competitiveness in the market. Efficient furnace operation, consistent quality control measures, and effective maintenance practices are crucial for maximizing the plant’s productivity. DRI plants often incorporate advanced automation technology to optimize process control and minimize downtime. The market for DRI has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for steel and the need for more sustainable ironmaking processes. DRI is mainly used as a feedstock in electric arc furnaces, which are commonly used in the production of long steel products, such as reinforcing bars, wire rods, and structural sections. The use of DRI in EAFs reduces the dependence on scrap metal and lowers energy consumption, resulting in cost savings for steel manufacturers.
buy iron
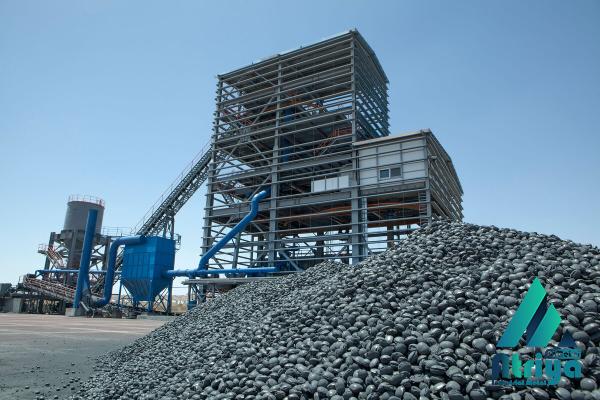 The global DRI market is highly competitive, with several key players dominating the industry. Major DRI producers operate large-scale plants and have established partnerships with steel manufacturers around the world. These companies invest heavily in research and development to enhance their production technologies and maintain a competitive edge in the market. The expansion of DRI capacity in emerging economies, such as India and the Middle East, has also contributed to the growth of the global DRI market. In conclusion, direct reduced iron plants play a vital role in the steel industry by producing high-quality iron nuggets through the reduction of iron ore. These plants offer several advantages over traditional blast furnace ironmaking, including lower environmental impact, improved steel quality, and adaptability to market demand. The construction and operation of DRI plants require significant investments in infrastructure and technology. The global DRI market has been growing steadily due to the increasing demand for steel and the need for more sustainable ironmaking processes.
The global DRI market is highly competitive, with several key players dominating the industry. Major DRI producers operate large-scale plants and have established partnerships with steel manufacturers around the world. These companies invest heavily in research and development to enhance their production technologies and maintain a competitive edge in the market. The expansion of DRI capacity in emerging economies, such as India and the Middle East, has also contributed to the growth of the global DRI market. In conclusion, direct reduced iron plants play a vital role in the steel industry by producing high-quality iron nuggets through the reduction of iron ore. These plants offer several advantages over traditional blast furnace ironmaking, including lower environmental impact, improved steel quality, and adaptability to market demand. The construction and operation of DRI plants require significant investments in infrastructure and technology. The global DRI market has been growing steadily due to the increasing demand for steel and the need for more sustainable ironmaking processes.










Your comment submitted.