Direct reduction iron ore is a method of producing iron from iron ore without using traditional blast furnaces. This process, also known as direct reduction, involves the use of natural gas or coal as a reducing agent to convert iron ore into a sponge iron product. The sponge iron is then further processed to create finished steel products. Direct reduction iron ore has gained popularity in recent years due to its energy efficiency, lower carbon emissions, and flexibility to use a wide range of iron ores. It offers numerous advantages over traditional blast furnace methods, making it a sustainable and economically viable option for steel production. The direct reduction process begins with the preparation of iron ore, typically in the form of pellet or lump ore. The ore is then charged into a rotary kiln or shaft furnace, where it is heated to high temperatures. The reducing agent, usually natural gas or coal, is injected into the kiln, and the iron ore reacts with the reducing agent to form sponge iron.
iron
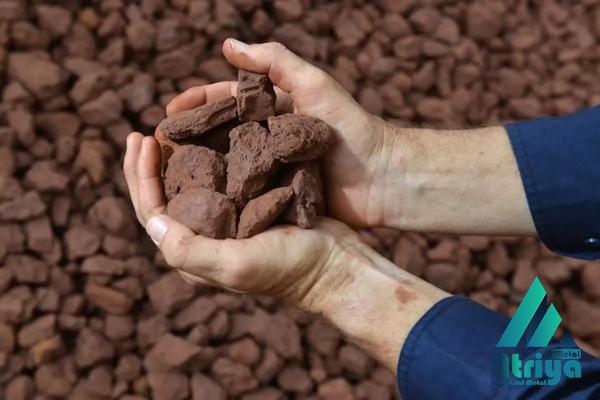 The sponge iron produced in the direct reduction process contains impurities such as gangue minerals and non-iron elements. These impurities need to be removed through further processing to produce high-quality steel. The sponge iron is first cooled and then passed through magnetic separators to remove any magnetic impurities. It is then smelted in an electric arc furnace or a basic oxygen furnace to remove remaining impurities and produce liquid steel. Direct reduction iron ore offers several advantages over traditional blast furnace methods. Firstly, it is more energy-efficient as it requires lower temperatures compared to blast furnaces. This leads to significant savings in fuel consumption and reduced carbon emissions. Additionally, the direct reduction process is more flexible in terms of the type of iron ores it can utilize, including lower-grade ores and fine ores, which are not suitable for blast furnace operations.
The sponge iron produced in the direct reduction process contains impurities such as gangue minerals and non-iron elements. These impurities need to be removed through further processing to produce high-quality steel. The sponge iron is first cooled and then passed through magnetic separators to remove any magnetic impurities. It is then smelted in an electric arc furnace or a basic oxygen furnace to remove remaining impurities and produce liquid steel. Direct reduction iron ore offers several advantages over traditional blast furnace methods. Firstly, it is more energy-efficient as it requires lower temperatures compared to blast furnaces. This leads to significant savings in fuel consumption and reduced carbon emissions. Additionally, the direct reduction process is more flexible in terms of the type of iron ores it can utilize, including lower-grade ores and fine ores, which are not suitable for blast furnace operations.
Specifications of iron
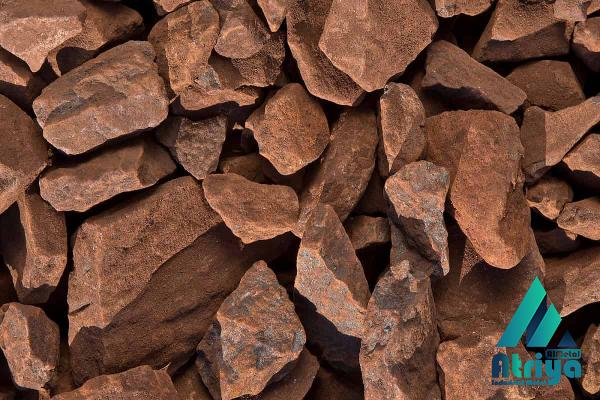 The direct reduction process also offers greater control over the production of steel. It allows for quick start-up and shutdown times, making it suitable for adapting to fluctuations in steel demand. This flexibility helps steel manufacturers to respond to changing market conditions and optimize their production schedules. In terms of sustainability, direct reduction iron ore has a lower environmental impact compared to traditional blast furnaces. The use of natural gas as a reducing agent reduces greenhouse gas emissions significantly. Additionally, the direct reduction process produces less solid waste and generates fewer by-products compared to blast furnace operations. Direct reduction iron ore has gained significant attention in regions with abundant natural gas resources, such as the Middle East and North America. These regions have invested in direct reduction plants to take advantage of their natural gas reserves and reduce their dependence on imported steel. Many direct reduction plants have been established in these regions, contributing to the growth of the direct reduction iron ore industry.
The direct reduction process also offers greater control over the production of steel. It allows for quick start-up and shutdown times, making it suitable for adapting to fluctuations in steel demand. This flexibility helps steel manufacturers to respond to changing market conditions and optimize their production schedules. In terms of sustainability, direct reduction iron ore has a lower environmental impact compared to traditional blast furnaces. The use of natural gas as a reducing agent reduces greenhouse gas emissions significantly. Additionally, the direct reduction process produces less solid waste and generates fewer by-products compared to blast furnace operations. Direct reduction iron ore has gained significant attention in regions with abundant natural gas resources, such as the Middle East and North America. These regions have invested in direct reduction plants to take advantage of their natural gas reserves and reduce their dependence on imported steel. Many direct reduction plants have been established in these regions, contributing to the growth of the direct reduction iron ore industry.
buy iron
 One of the most commonly used direct reduction technologies is the Midrex Process, which was developed in the 1960s. The Midrex Process uses natural gas as a reducing agent and operates in a vertical shaft furnace. It is renowned for its high reliability, flexibility, and ability to produce high-quality sponge iron. Another widely used direct reduction technology is the HYL/Energiron Process, which was developed in the 1950s. This process uses a mixture of gases known as reformed natural gas (RNG) as a reducing agent and operates in a moving bed reactor. The HYL/Energiron Process is known for its ability to process lower-grade iron ores and produce high-quality sponge iron. In conclusion, direct reduction iron ore is a sustainable and efficient method of producing iron and steel. The process offers numerous advantages over traditional blast furnace methods, including lower energy consumption, reduced carbon emissions, and greater flexibility in the use of iron ores. With advancements in technology and increasing global demand for steel, the direct reduction iron ore industry is expected to grow further in the coming years.
One of the most commonly used direct reduction technologies is the Midrex Process, which was developed in the 1960s. The Midrex Process uses natural gas as a reducing agent and operates in a vertical shaft furnace. It is renowned for its high reliability, flexibility, and ability to produce high-quality sponge iron. Another widely used direct reduction technology is the HYL/Energiron Process, which was developed in the 1950s. This process uses a mixture of gases known as reformed natural gas (RNG) as a reducing agent and operates in a moving bed reactor. The HYL/Energiron Process is known for its ability to process lower-grade iron ores and produce high-quality sponge iron. In conclusion, direct reduction iron ore is a sustainable and efficient method of producing iron and steel. The process offers numerous advantages over traditional blast furnace methods, including lower energy consumption, reduced carbon emissions, and greater flexibility in the use of iron ores. With advancements in technology and increasing global demand for steel, the direct reduction iron ore industry is expected to grow further in the coming years.










Your comment submitted.